Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in nearly every electronic device. Their quality directly affects the reliability and performance of the final product. If you’re a product designer or manufacturer working with a PCB manufacturer, you’ve likely encountered IPC Class 2 and Class 3 standards. But what do these classifications mean, and how do they impact your project? In this blog, we’ll dive into IPC Class 2 vs. Class 3, explaining their design rules and how they influence PCB quality.
At Blind Buried Circuits, we specialize in custom PCB manufacturing and adhere to IPC standards, ensuring high-quality PCBs tailored to your needs. Let’s explore how these classifications apply to your next project.
What Are IPC Class 2 and Class 3 Standards?
The IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries) establishes quality standards for PCBs, which are divided into three classes:
Class 1 (General Electronics): Applications with minimum reliability requirements, such as consumer electronics.
Class 2 (Dedicated Service Electronics): Products that are required to perform reliably, such as industrial or medical devices.
Class 3 (High-Performance Electronics): Such products that demand absolute reliability such as aerospace or military equipment.
Class 2 and Class 3 focus on functionality and long-term reliability, but the criteria are quite different.
Key Differences Between Class 2 and Class 3
- Tolerable Tolerances
Class 2: There can be minor cosmetic defects so long as functionality is not compromised.
Class 3: Perfect alignment is a requirement to ensure zero tolerance for defects in critical areas.
- Reliability Requirements
Class 2: For moderate reliability. They work satisfactorily but do not have a high shelf life in extreme conditions.
Class 3: It requires more robustness and performance even in extreme environments.
- Acceptance Criteria
Class 2: Lax acceptance criteria. This means electrical performance is the most important criterion, while aesthetics takes a back seat.
Class 3: Detailed acceptance criteria to ensure accuracy, durability, and zero defects.
How Design Rules Impact PCB Quality
The PCB design rules form an essential part of satisfying the necessary IPC classification. Some factors, such as trace width, spacing, and hole size, will be critical in determining manufacturability and quality. Let’s break these down into details:
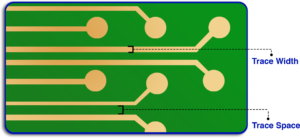
- Trace Width and Spacing
Class 2: Will accept traces a little wider with some tolerance on spacing.
Class 3: Must be more tightly tolerated to support high-density interconnects for reliability.
At Blind Buried Circuits, we accommodate trace widths as low as 2/2 mils to meet Class 3 standards for demanding applications.
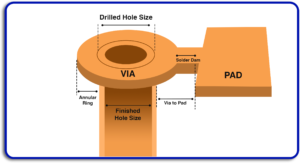
- Vias and Hole Tolerances
Class 2: Accepts minor deviations in hole alignment and plating thickness.
Class 3: Demands precise alignment and consistent plating to prevent electrical failures.
Our advanced PCB layout process ensures compliance with even the strictest Class 3 requirements.
- Material Selection
Class 2: Suitable for standard FR4 materials.
Class 3: Frequently utilizes high-grade materials such as Rogers or Megtron for enhanced thermal and electrical performance.
We can create custom stack-ups that are specialized to fit both classifications.
Benefits of Partnering With Blind Buried Circuits
We at Blind Buried Circuits can provide you with customized PCB manufacturing according to both the IPC Class 2 and Class 3 standards. Here’s why you should choose us:
Fast Turnaround: We are specialists in short lead times, which help in expediting the completion of projects.
Custom Solutions: From photos to full production volume, we can accommodate all your customized requirements.
High-Volume Capability: Our facilities support high-density interconnects, multi-layer PCBs, and specialized exotic materials for the most advanced designs.
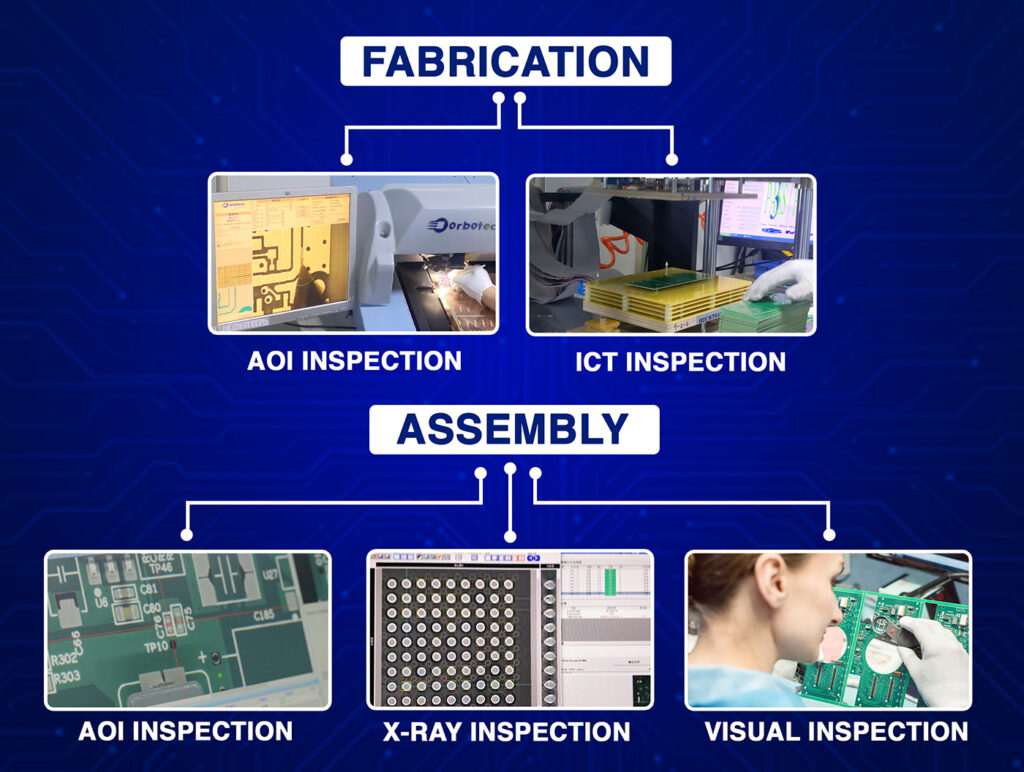
Quality Certification: ISO and IPC Certifications ensure that every board exceeds class standards.
Browse our capability statements and see how we may help you with your next project.
Why Choose the Right IPC Class for Your Project?
The choice between Class 2 and Class 3 depends on your products end-use. Here’s a quick comparison to guide your decision:
| Feature | IPC Class 2 | IPC Class 3 |
| Reliability | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to stringent standards |
| Applications | Industrial, medical devices | Aerospace, military, high-stress equipment |
| Lifespan | Suitable for standard use | Extended lifespan in extreme conditions |
Choosing the wrong class can lead to over-engineering or insufficient durability, both of which affect your budget and performance.
Understanding Class 2 and Class 3 of the IPC standard is essential to getting the appropriate PCB for your application. Design rules, material selection, and inspection protocols are all considered when meeting these classifications. Whether you want moderate reliability or top performance, a partnership with a renowned PCB manufacturer like Blind Buried Circuits guarantees success.We offer the best end-to-end PCB layout and manufacturing services, designed according to your requirements. We cater to prototypes as well as the most complex designs. Contact us today to discuss your project and experience seamless custom PCB manufacturing like never before.
To learn more about Class 2 and Class 3, don’t hesitate to contact our sales team at [email protected].