Printed Circuit Boards, or PCBs, form the core of every electronic device we use today, ranging from smartphones to complex industrial machinery. Behind the successful functioning of these PCBs lies meticulous planning, manufacturing, and quality control. Adherence to IPC standards is one of the cornerstones of ensuring consistency and quality in PCB production.
Whether you’re venturing into custom PCB manufacturing or scaling up PCB production, understanding IPC standards is crucial for both manufacturers and consumers. This article explores how these standards impact the process and why they are essential.
What Are IPC Standards?
IPC, previously known as the Institute for Interconnecting and Packaging Electronic Circuits, is a global standard-setting body for PCB assembly, design, and performance. This means that every stage of PCB manufacturing, from design to the final product, meets quality and reliability benchmarks.
Why Are IPC Standards Important?
IPC standards are essential because they provide a universal framework that manufacturers and designers follow to ensure:
Quality Assurance
The IPC standards are set to ensure high-quality PCBs that will perform as needed in different applications.
Reliability
Compliance with these standards decreases the likelihood of failure, an important requirement in industries that require both safety and precision, such as aerospace or healthcare.
Global Compliance
Compliance with the IPC standards ensures that PCB manufacturers can easily produce units that meet international standards, which makes it easier to export.
Role of IPC Standards in Custom PCB Manufacturing
Custom PCBs are essential in today’s electronics landscape, providing tailored solutions for specific applications in industries like medical devices, automotive systems, and consumer gadgets. Unlike mass-produced PCBs, custom designs often require unique specifications to fit precise functional requirements. This variability makes adherence to IPC standards even more critical in custom PCB manufacturing, ensuring quality and reliability at every step.
Enhancing Design Accuracy
Custom PCBs often involve complex layouts to meet specific needs, such as accommodating unique components or fitting into unconventional form factors. IPC standards guide manufacturers in designing these layouts, ensuring they:
- Maintain proper spacing between conductive paths.
- Follow defined tolerances for features like vias and pads.
- Account for thermal management and signal integrity.
These guidelines reduce the risk of design flaws, leading to faster prototyping and fewer iterations. As a result, manufacturers save time and resources while delivering a product that meets performance expectations.
Streamlining the Manufacturing Process
Custom PCBs typically require special materials, components, or processes. IPC standards help manufacturers:
- Select materials compatible with the board’s intended use, such as high-temperature substrates for industrial applications.
- Optimize production techniques like etching, plating, and drilling, ensuring consistent results.
- Implement standardized testing protocols to verify that the final product meets the desired specifications.
By adhering to these practices, manufacturers can handle the complexities of custom designs while maintaining efficiency and minimizing errors.
Ensuring Durability and Reliability
Custom PCBs are often deployed in critical applications where failures can have severe consequences, such as medical equipment or aerospace systems. IPC standards establish rigorous testing and quality control measures, including:
- Thermal Cycling: Ensures PCBs can withstand temperature fluctuations.
- Electrical Testing: Verifies circuit integrity under operational conditions.
- Mechanical Stress Tests: Confirms durability against vibrations or physical impact.
These procedures guarantee that custom PCBs perform reliably even under demanding conditions, instilling confidence in their use.
Supporting Scalability and Future Upgrades
For businesses developing custom PCBs, scalability is often a long-term goal. IPC standards provide a framework for creating designs that can be easily scaled or upgraded. For instance, following IPC guidelines for trace width and layer stacking ensures that a PCB design can be adapted for higher performance without requiring a complete redesign.
Additionally, adhering to IPC standards makes it easier for manufacturers to collaborate with different partners or transition to new suppliers, as the guidelines ensure compatibility and consistency across the industry.
Building Trust and Customer Confidence
Clients investing in custom PCBs often seek assurance that their products meet the highest quality standards. By following IPC guidelines, manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to delivering reliable, high-performance PCBs. This transparency builds trust, strengthens customer relationships, and enhances a manufacturer’s reputation in a competitive market.
Addressing Unique Challenges in Custom Designs
Custom PCBs come with their own set of challenges, such as limited production runs or unconventional specifications. IPC standards help address these issues by:
- Providing flexibility to adapt design rules for specific needs.
- Establishing clear communication protocols between designers and manufacturers.
- Offering comprehensive testing methodologies to validate unique features.
For example, if a custom PCB requires a mix of high-power and low-power circuits, IPC guidelines help ensure that the design prevents issues like electromagnetic interference (EMI) or thermal hotspots.
Benefits of IPC Standards for Custom PCBs
Design Accuracy
The IPC standard guides designers to create a PCB layout that minimizes errors, thereby improving the performance and lifespan.
Productivity
Manufacturers use IPC guidelines to streamline production, which reduces delays due to design or material inconsistencies.
Customer Satisfaction
Meeting IPC standards gives customers confidence in knowing they are getting a reliable and high-performing product.
IPC Classifications: What They Mean for PCB Production
IPC standards classify PCBs into three main categories based on their application and required reliability:
| IPC Class | Application | Reliability |
| Class 1 | Consumer electronics (e.g., toys) | Basic performance requirements |
| Class 2 | Industrial tools, communication devices | Enhanced reliability |
| Class 3 | Aerospace, medical devices | High reliability, zero defects |
These classifications help manufacturers tailor their processes to meet the specific demands of each industry. For instance, PCB production for Class 3 applications involves stricter testing and quality control.
Ensuring Compliance: Challenges and Best Practices
Adhering to IPC standards is not without its challenges. Here’s how manufacturers overcome common hurdles:
1. Training and Expertise
Challenge: IPC standards can be complex for new designers and manufacturers.
Solution: Regular training and certification programs keep the teams updated with the latest standards.
2. Material Selection
Problem: The use of low-grade materials may make them non-compliant.
Solution: Materials must always come from the right sources, reputed suppliers who follow IPC guidelines.
3. Testing and Inspection
Problem: Testing methods become less effective in identifying defects.
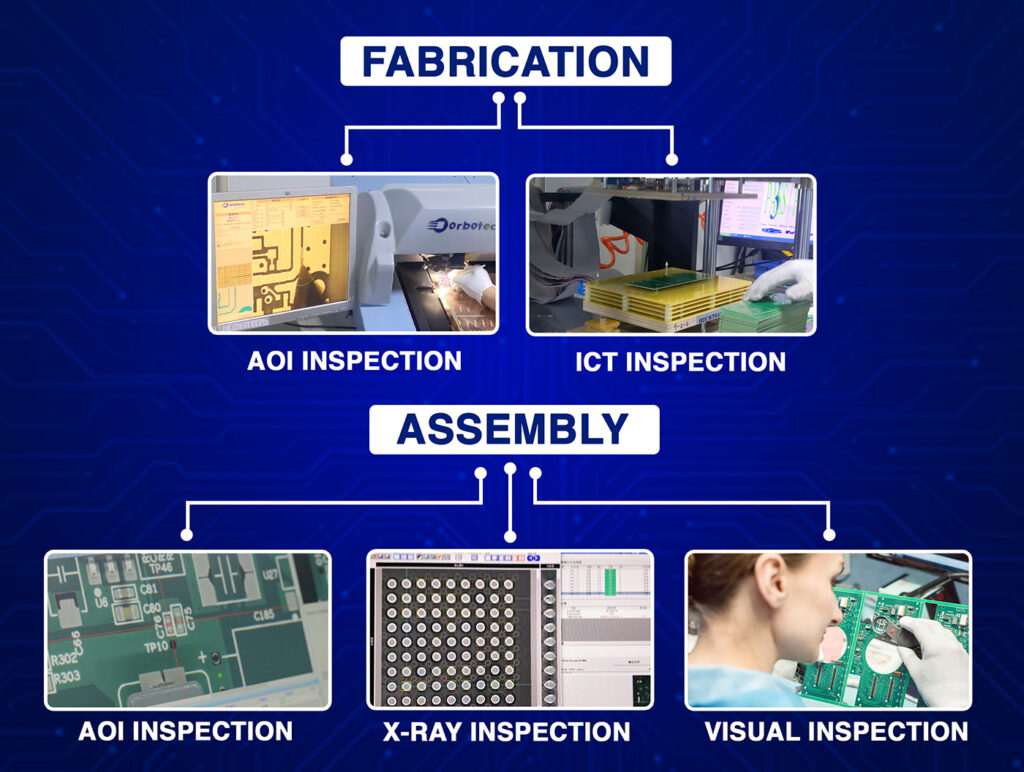
Solution: Advanced testing methods, such as automated optical inspection (AOI), must be used to ensure that each PCB meets IPC standards.
Impact on Global Trade and Standardization
One of the most important benefits provided by IPC standards is that they help ease international trading. Manufacturers complying with standards can export their products internationally without further testing or certifications, thus speeding up launches and minimizing costs.
Besides, IPC standards level the playing field. It is easier for SMEs engaged in custom PCB manufacturing to compete with the other large players when they can provide evidence of adherence to benchmark standards recognized internationally.
A Closer Look: IPC Standards and Eco-Friendly PCB Manufacturing
Environmental friendliness is also a vital aspect in IPC standards which addresses environmentally friendly practices by PCB manufacturers. Manufacturers of PCBs are encouraged to use lead-free materials, reduce waste, and use an energy-efficient process.
By following these standards, companies not only follow the environmental laws but also attract environment-conscious customers.
IPC standards are the foundation of the PCB industry and ensure quality, reliability, and global compatibility. Whether custom PCB manufacturing or mass production, the standard helps streamline processes, reduce errors, and make customers believe in the products. Adopting IPC standards has become a norm, especially in today’s competitive market. By embracing compliant manufacturers and keeping oneself abreast of the guidelines to follow, firms are assured of long-term achievements in the industry, and the products presented to their clients shall always be of high quality. At Blind Buried Circuits, our strength in custom PCB production and advanced PCB routing guarantees great results for your project. Contact us now, and let’s bring those innovative designs to life!