The aerospace industry has specific requirements regarding the capabilities and features of printed circuit boards (PCBs). These boards have to be of high quality and thermally reliable since they are exposed to extreme conditions of high altitudes, vibration, and temperature changes. Electronics used in the aerospace sector need to have absolute reliability and functionality. To achieve long-lasting reliability in aerospace PCBs, thermal management has to be properly executed and planned.
This blog post will elaborate on some of the most effective thermal management processes in PCB design for aerospace. It includes flex circuits, board manufacturers, flexible PCB fabrication, and other techniques for aerospace PCB design, fabrication, and increased performance and durability.
Understanding Thermal Management in Aerospace PCBs
Importance of Thermal Management
Aerospace activities use modified PCBs, as opposed to consumer electronics, which utilize standard PCBs. These modified PCBs have to withstand harsh temperatures ranging from -200 degrees Celsius in space to over 200 degrees Celsius in high-speed aircraft. If the electrical parts are not properly dissipated, they can fail or degrade, which can create catastrophic consequences for communication systems like navigation and onboard computers.
- Aerospace PCBs: Considered to Have the Following Heat Sources:
- Power Electronics: The converters, amplifiers, and RF systems that are utilized as parts.
- Processors and FPGAs: Localized cooling can be brought on by high-speed data processing.
- Batteries And Energy Storage Devices: Able to generate heat, which can have an impact on the performance as well as the overall life of the device.
- Antenna And RF Modules: Excess heat from efficient wireless communication systems also need to be dispensed with.
Improved Heat Management for Aerospace PCBs
1. Thermal Expansion – Warping
Incorporating aerospace systems is subjected to intense heat and the severe cold of space. In addition, PCBs ought to be manufactured from low thermally expandable materials that do warp or induce mechanical strain.
 2. Condensed Liquid Coolant
2. Condensed Liquid Coolant
Many traditional cooling devices like fans or liquid cooling devices are ineffective against several aerospace solutions. Instead, liquid cooling necessitates a mix between passive and active thermal management. PCBs will have to work between the extremes.
3. Improved Cooling Measures
With more compactness of frames with additional layers of bigger components, aerospace systems’ PCBs do improve, but not without heat aiding in the moderating. With these gaps, cooling can be advanced significantly.
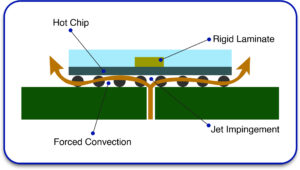
Improved Heat Management for Aerospace PCBs
1. Using Different Materials for Each PCB
- Polyimide Flex PCBs: These boards possess the right amount of flexibility and high-temperature stability, therefore making them fit for use in aerospace.
- MCPCB: The integration of copper or aluminum cores on these boards enhances heat dissipation.
- Ceramic PCBs: These PCBs are thermally shock-resistant and have excellent thermal conductivity. They are a PCB specialty, after all.
- PTFE RF PCBs: The heat capabilities on these boards make them ideal for use in satellite communication.
2. Flex And Rigid-Flex Designs on Circuit Boards
Because flex circuit board designers play a key role when engineering aerospace PCBs, they manufacture parts that are lightweight and highly durable, capable of withstanding sensitive applications. In this segment, we shall highlight Flex PCBs and their benefits within the aerospace industry. Afterward, we will delve into the incorporation of thermal vias, embedded heat spreaders, and die-cast aluminum heat sinks.
Flex PCBs are useful in any industry, but the aerospace industry benefits the most from it for these reasons:
- Superior heat control due to the thin, flexible design.
- Excellent reliability in multi-layered dense designs next to lower mechanical failures thanks to higher shock and vibration resistance.
- Lowers the weight and helps enhance system performance. Aerospace systems may benefit from the mechanical, structural, and thermal performance enhancement afforded by two-dimensional flexible PCB design techniques. For example, engineers can design PCBs that are flexible and can be placed in the most thermally efficient locations.
3. Incorporating Thermal Vias
Thermal vias are essential elements in routing thermal energy away from powerful components and distributing it to the lower portions of the PCB. These via holes, normally plated, act as channels for heat’s transfer to the ground or power layers.
Best Practices for Thermal Vias:
Instead of a single large via, use a number of small ones to increase efficiency in heat insulation. Take account of placing thermal vias on the interior of copper ground planes that are in the position of aiding the overheating of the structure. Enable the position of vias in as much as they are likely to help in the checking of heat over the thermal hotspots.
4. Using Embedded Heat Spreaders and Heat Sinks
In the case of aerospace PCBs, the most sensitive areas are typically shielded by heat spreaders and heat sinks integrated into the system.
Best methods for enhancing dissipating heat:
- These aid with the Copper Spreaders: these increase the thermal management of multi-layer PCBs for aerospace devices.
- Aluminum die-casted heat sink: These can significantly improve satellite PCB avionics system passive cooling.
5. Enhancing conductivity with Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
TIMs make heat transfer between parts and PCB surfaces more effective. These materials support the cooling efforts by minimizing thermal resistance.
Some Common TIMs Used In Aerospace PCBs Are:
- Silicone-based thermal pads enable uniform heat distribution.
- Phase Change Materials (PCM) for extreme heat conditions.
- Graphene TIMs complement materials needed while being extremely light.
6. The Newest Strategy of PCB Manufacturing
PCB manufacturers utilize new construction strategies to enhance the thermal control of aerospace PCBs.
Some New Age Methods Include:
- Back drill for thermal relief works by preventing the accumulation of heat, which requires the elimination of extra copper.
- Laser drilled micro vias as a feature for aerospace HDI PCBs improves heat conduction.
- Selective plating for high-powered aerospace electronics increases the range of systems aircraft can operate under.
7. Techniques of Active Cooling
For other high-powered applications in aviation, active measures might augment passive ones.
Cooling Examples for Aerospace PCBs:
- TECs or Tero Electric Coolers utilize current to extract heat away from the board component.
- Some PCBs include sealed channels with liquid coolant for high-temperature scenarios.
- In avionics, hot air flow control systems are utilized for temperature regulation.
Learn About: Advancements in PCBAs for Aerospace Thermal Control Systems
What Makes Flex PCBs Perfect For Use In Satellites?
Flex PCBs tend to be integrated into the fabrication of satellite PCBs because of their high reliability, low weight, and their ability to sustain space radiation.
Benefits of Flex PCBs In Spacecraft:
- This technology is able to withstand both very high and very low extremes of temperature and still function normally.
- High resistance to radiation in the satellite environment.
- High durability against micro-vibration in space missions.
- Lightweight construction contributes to improving payload efficiency.
- Flexible PCB fabrication methods enable reliable performance in low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites, geostationary satellites, and deep space missions.
Essential Considerations When Creating PCBs for Aerospace Applications
Aerospace engineers need to take into account the specificities of thermal PCB design for aerospace applications to guarantee proper mission execution together with thermally dependable solutions.
Factors To Consider When Heating:
- Conducting thermal analysis before the design is a must: Make sure thermals are simulated before the actual construction in order to avoid overheating.
- Placement of components: Power components should be located near the heat sink and the vias.
- More shielding and insulations: Better precision should be used when managing electromagnetic interference (EMI) along with high-power heat components.
- IPC and aerospace standards: Provide IPC-6012 Class 3A along with NASA PCB outline and description requirements.
Through incorporating flex circuit board manufacturers, flexible PCB fabrication, and innovative cooling designs for flex PCBs, control over space and aviation conditions is greatly enhanced.
This ensures more control over the dependability and life span of aerospace PCB solutions. Blind Buried Circuits leads the industry with new methods of aerospace PCB manufacturing and develops custom thermal solutions for very high-end performance applications. We deliver the industry’s best flexible and dependable innovative PCB solutions to clients designing satellites and avionics systems PCBs.