Manufacturing a quality PCB is more than just generating a schematic and routing traces. A PCB design review is an essential part of the process that ensures that the board works correctly, passes all manufacturing requirements, and does not require expensive repairs or fixes. Whether you are collaborating with a PCB board manufacturer or doing custom PCB production in-house, clean-up is necessary for your layout to be as reliable and efficient as possible.
This guide focuses on PCB design review and layout clean-up procedures, ranging from PCB design quality checklists to PCB layout change suggestions that reduce the possibility of mistakes and make manufacturing more manageable.
Why is PCB Design Review and Layout Clean Up Important?
Designing the review for your PCB is critical. Drawing out these details may result in design flaws, delays in production, and even failures of functionality altogether. Some of the problems that stem from poor layout clean-up include:
- Issues with the integrity of the signal due to the improper routing of traces.
- Problems with voltage drops or overheating caused by the loss of power.
- Ignored construction mistakes such as pads not being there, bad drill sizes, or improperly placed components.
- Other forms of electromagnetic interference (EMI) result from weak grounding or signal crosstalk.
- Difficulties during assembly cause defects in the solder joints or components being placed incorrectly.
Adhering to these practices is critical so that your PCB board manufacturer can produce and assemble your design. Following these practices will ultimately improve production efficiency.
Essential Focus Points for Your PCB Design Review
A well defined PCB design review procedure assures that your design accomplishes the targets of performance, reliability, and manufacturability. Make sure to review these most important areas:
1. Verification of Component Placement:
Proper placement guarantees that your board is simple to assemble, test, and maintain.
Best Practices:
- Place high-power components near heat dissipation areas
- Maintain sufficient space between components for easy soldering
- Place sensitive analog components away from high-speed digital components
- Position connectors where they can be easily reached in the final assembly
- Mark fiducials to aid automated assembly machines
Tip for layout cleanup: Use a design rule check (DRC) in your PCB CAD to find placement issues.
2. Enhancing Ground and Power Planes
For signal integrity and noise mitigation, a well-defined power and ground structure is paramount.
Best Practices:
- Enhance stability further with dedicated ground planes to reduce noise.
- Widen power traces more than signal traces to handle current loads easily.
- Do not have narrow necks in power planes that will reduce the voltage.
- Reduce EMI with minimised loop areas with ground connections.
- Control IC voltage with a stable supply by distributing decoupling capacitors near the power pins of ICs.
Tip for layout cleanup: Check voltage stability with a power integrity analysis tool.
3. Improving signal routing
Improving signal routing and optimizing trace layouts signals and trace optimization placement are two fundamental problems in PCB design. Poorly routed traces can result in crosstalk, crosstalk reflections, and timing errors.
Best Practices:
- Minimize high-speed traces as much as possible to mitigate delay.
- Use consistent widths of traces for impedance control.
- Place differential pairs together to increase signal integrity.
- Avoid sharp angles; use 45-degree angles instead to lessen signal reflections.
- Use guard traces and shielding for touch signals.
- Run a signal integrity check before production for detection of routing errors to clean up the layout.
4. Checking via positions and layer stack up
Via placement plays a critical role in multilayer PCBs. Incorrectly placed vias can result in defects during manufacture.
Best Practices:
- Be cautious when using via-in-pad as it may require more manufacturing steps.
- Place thermal relief vias around power components.
- Do not place vias too close to solder pads as this leads to wicking.
- Place vias in the laser equipment layer for high-density custom PCB production where space is limited.
- Ensure that the stack of the layer is optimized for impedance and thermal control.
- Make sure the sizes of the via holes match the PCB board manufacturer’s specifications.
5. Avoiding silkscreen and solder mask problems
Soldering accuracy and readability of the PCB are affected by the silkscreen and solder mask layers.
Disclaimer: The following section restructures the layout of components within a PCB and offers solutions to manage layout errors for more efficient fabrication.
Best Practices :
- Check that labels are not overlapping each other and are easily readable.
- Ensure that the silkscreen is not on top of any of the pads to avoid mistakes when printing.
- Ensure that the silkscreen is a different color than the PCB for all other materials.
- Check the solder mask openings for excessive solder bridges once the solder is done.
- Specify areas where any interference with soldering will not be practiced.
Tip: DFM can be used to verify silkscreen and solder mask placement for easier clean-up.
Performing a Thermal Analysis
Poorly managing thermal features of a system may lead to overheating, which causes damage to components.
Best Practices:
- Place thermal via underneath components that generate a lot of heat.
- For better dissipations, add heat sinks or metal core layers.
- Increase the copper thickness in power planes to ease the flow of electric current.
- Allow separation between nearby power components to ease local hotspots.
- For high-powered designs, consider using forced air cooling or liquid cooling.
Tip: Perform a thermal simulation to understand where overheating may occur for more efficient clean-up.
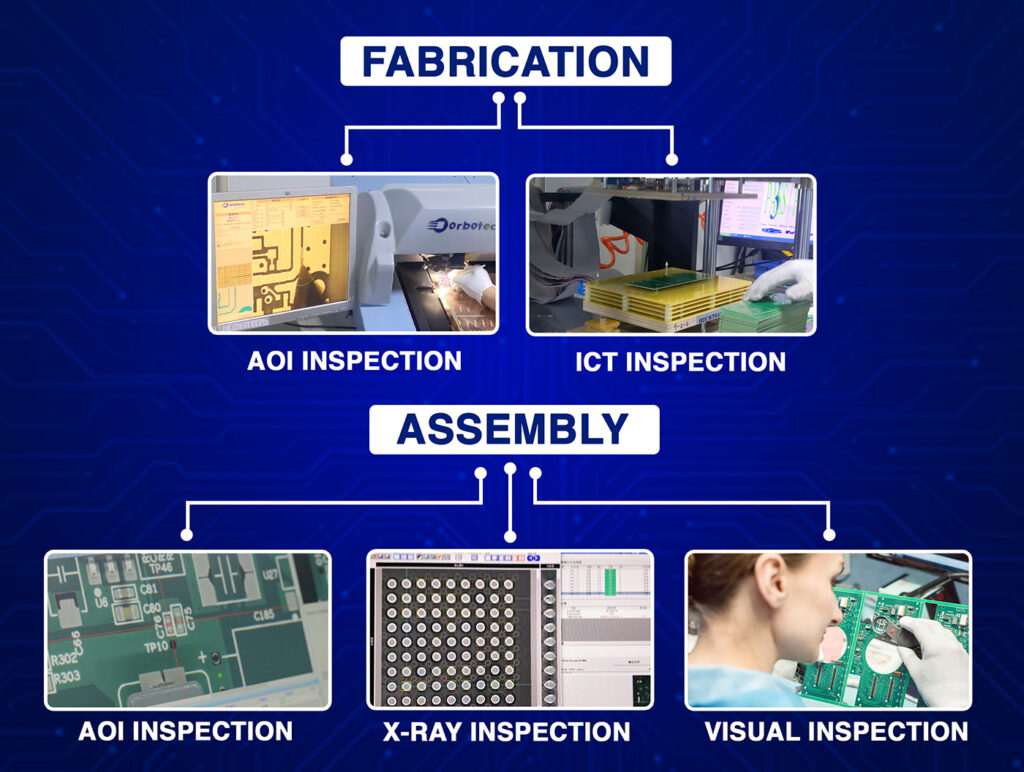
Common PCB Design Quality Checks Before Fabrication
Once designed on the layout, the PCB design quality check is useful in reducing issues when manufacturing.
Design Rule Check (DRC) and Electrical Rule Check (ERC):
- Verifying trace width, space, and via clearances
- Make sure that connected nets and floating copper are checked.
- Ensuring clearances for high-voltage traces.
Design For Manufacturability (DFM) Check:
- Ensure pad size is consistent with the PCB board manufacturer’s requirements.
- Drill-to-copper clearance check.
- Check the panelization optimization for economical production.
Assembly and Testability Review:
- Checkpoint placement for easy troubleshooting.
- Check the component’s placement concerning their orientation.
- Check the board’s compatibility with the mechanical enclosures.
Complete the Process: Generate a Gerber file, which will be sent to the PCB board manufacturer for review before production.
How To Improve PCB Layout For Better Performance?
An optimized PCB layout increases efficiency, reliability, and ease of manufacturing.
Shrink PCB Size While Retaining Optimal Performance:
- Implement multilayer boards for space optimization.
- Strategically place components to enable compact routing.
- Reduce ground copper islands while allowing proper copper ground continuity.
Enhance Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC):
- Use noise-reducing ground planes to minimize noise.
- Insert ferrite beads on the power lines.
- Protect RF-sensitive traces by covering them with copper pours.
Enhance the Cost Efficiency of Your PCB:
- Utilize normal PCB materials for cost reduction.
- Limit the use of vias for easier production.
- Maximize batch production for cheaper per-unit prices.
Tip: To reduce expenses, work closely with a custom PCB production partner.
Why Is PCB Design Review and Layout Clean-Up Important?
There is an overall improvement in reliability with reduced errors, overall better performance, faster manufacturing with the removal of production bottlenecks, and lower costs with material and rework waste being further reduced. These guidelines will help designers and others who collaborate with PCB board manufacturers to achieve excellent design services without mistakes.
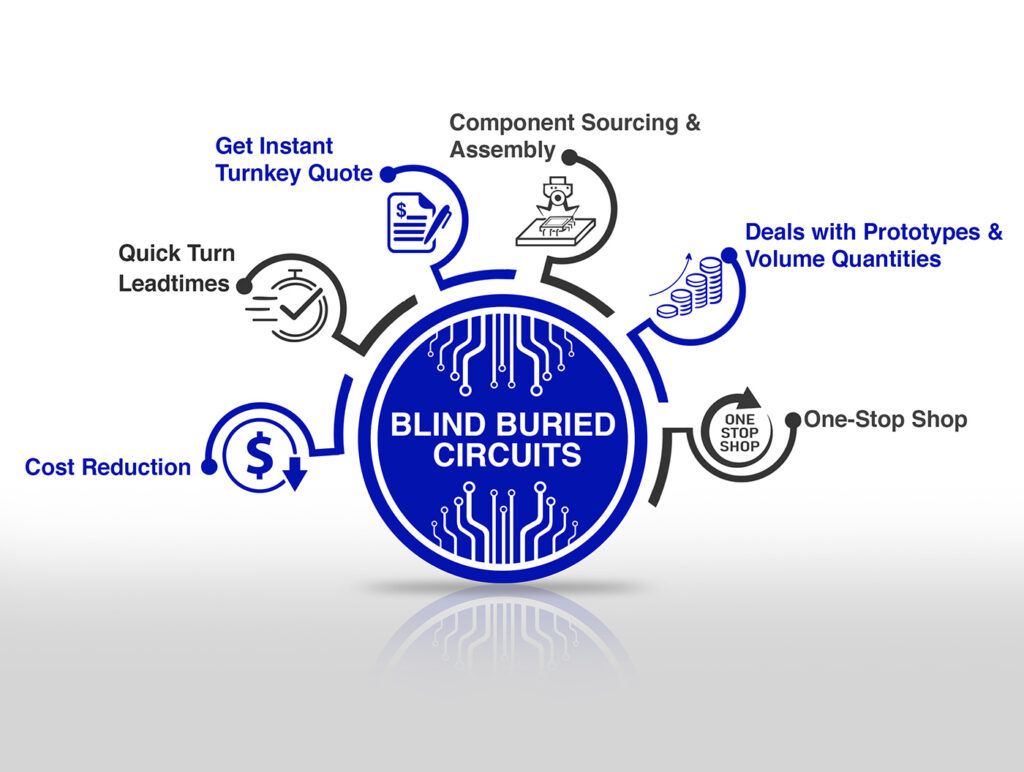
Blind Buried Circuits is your go-to custom PCB manufacturer, offering unparalleled assistance with PCB design review and layout optimization. Contact us today, and let us help you with your next project.