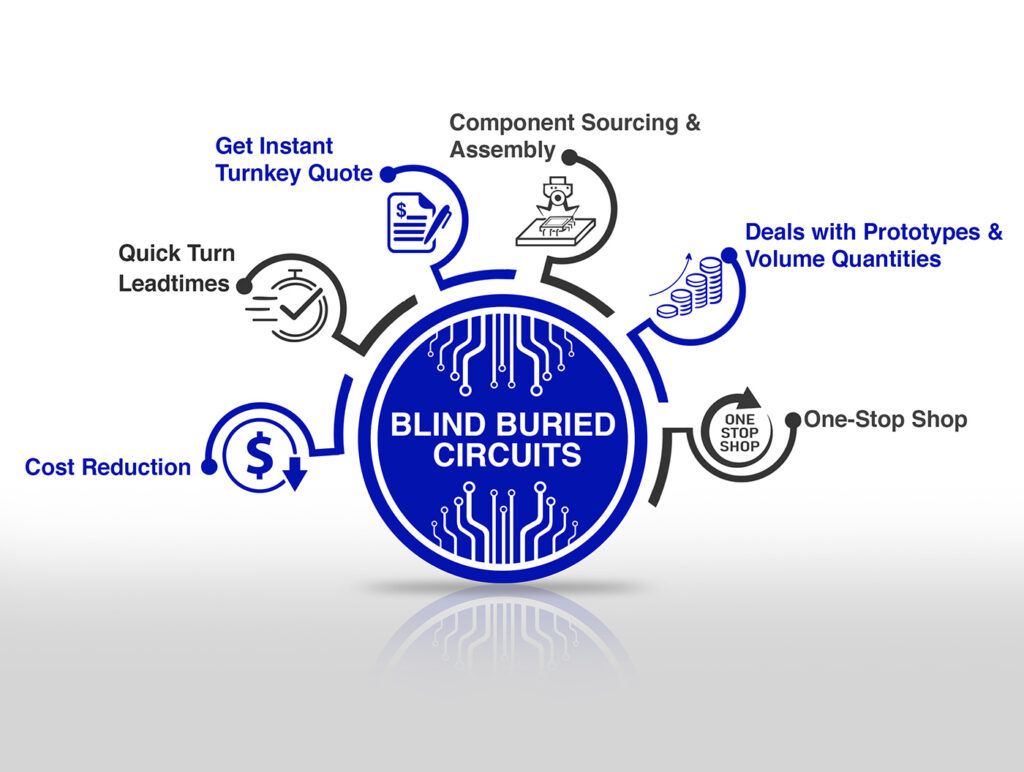
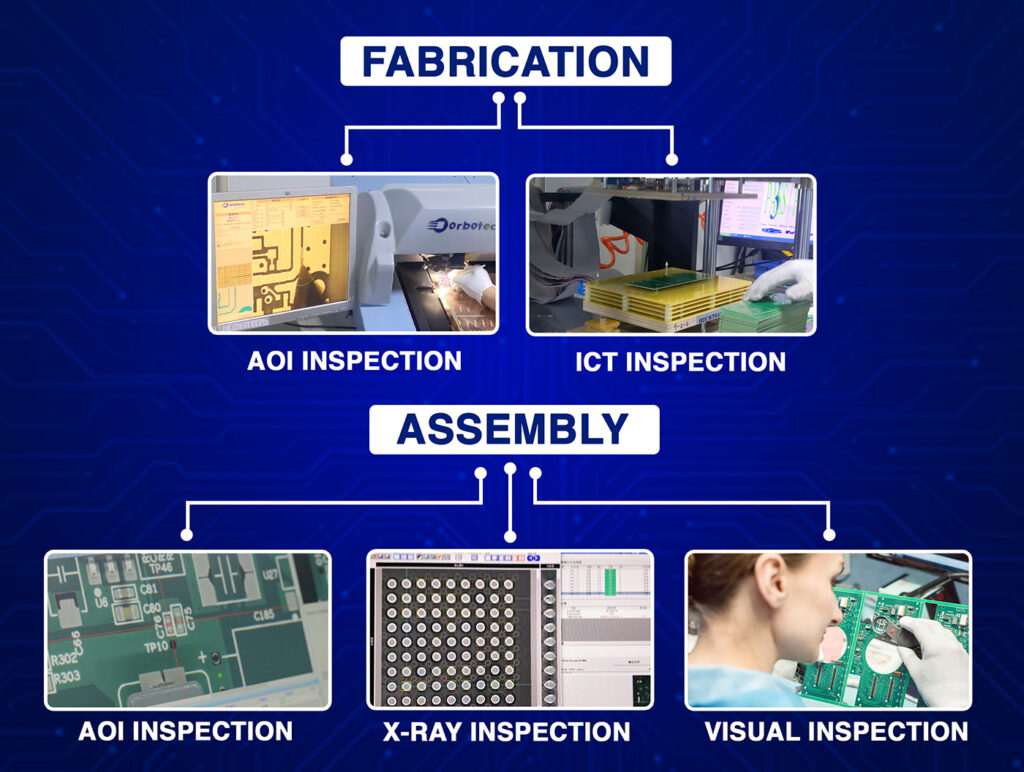
In printed circuit board fabrication, accuracy is paramount. One of the critical aspects of success in the final product is the use of slots and cutouts, all of which contribute to the functionality and mainly fulfil the design specifications. It has been mainly applied in connection with particular shapes or connectivity. Blind Buried Circuits offers premium quality PCB fabrication and assembly services. The PCB can have advanced flexible PCB fabrication in the most complex designs so that the products come with utmost precision and reliability.
Let us explore some techniques for making slots and cutouts in PCB manufacturing and their applications to advanced electronic designs.
Slots and Cutouts in PCBs: An Overview
Slots and cutouts refer to non-circular openings within a PCB. They are designed to accommodate components, improve fit within enclosures, or meet specific design requirements. Slots are elongated openings, while cutouts can take on various shapes, such as rectangles or custom configurations.
Common Reasons for Slots and Cutouts
- Component Placement: Provide space for connectors, mounting brackets, or other components.
- Thermal Management: Enhance heat dissipation by allowing airflow.
- Weight Loss: Reduce the weight of the board for aerospace or consumer electronics applications.
- Mechanical Fit: Locate the board within a housing or enclosure.
Slotting and Cutout Methods
The techniques for slotting and cutouts depend on the nature of the board material, the complexity of the design, and the production volume. This is a list of commonly used techniques:
Drilling
Drilling is a common technique for slotting. With CNC machines, manufacturers make long holes by drilling multiple overlapping circular holes. This technique is highly accurate and is commonly used for rigid and flexible PCB manufacturing.
Advantages:
Accurate outcome.
Good for small and medium-sized production.
Disadvantages:
Longer time for complex designs.
Routing
Routing is a technique where a milling machine is used to carve out slots and cutouts. It is the best technique for making custom shapes and large openings.
Advantages:
Allows complex shapes.
Faster than drilling for larger openings.
Limitations:
Needs advanced equipment.
Slightly less precise at edges than drilling.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting uses high-powered lasers to create slots and cutouts, particularly for flexible PCB fabrication where precision and minimal thermal impact are critical.
Advantages:
High precision.
Reduces stress on flexible materials.
Limitations:
More expensive.
Not readily available in some facilities.
Punching
Punching is an excellent technique for mass production. It employs a die to punch out slots and cutouts in one stroke.
Advantages:
Very fast.
Cheap for volume production.
Limitations:
Die-making involves a significant setup cost.
Only standard shapes are possible.
Applications of Slots and Cutouts
Slots and cutouts are used across industries, enhancing the PCB’s functionality and reliability.
Automotive Industry
Hold connectors and sensors.
Lightweight for better fuel efficiency.
Telecom and IoT Devices
Improve heat dissipation for high-performance systems.
Aerospace:
Lighten PCBs while maintaining structural integrity.
Medical Devices: Support accurate placement of sensitive components.
Consumer Electronics: Fit compact designs with advanced aesthetics.
Designing PCBs with Slots and Cutouts
Adding slots and cutouts to a PCB design should be done with planning and attention. Here are some general steps:
Define Specifications Clearly: Indicate slot and cutout dimensions, shapes, and tolerances in design files.
Use Compatible Materials: Make sure the board material is suitable for the intended fabrication method, especially for flexible PCB fabrication.
Collaborate with Manufacturers: Work closely with your PCB manufacturer to validate the design’s feasibility while ensuring that it meets industry standards.
Optimize for Assembly: Slots and cutouts should not interfere with either the placement of components or soldering processes.
Challenges and Solutions
- Alignment Issues
It can compromise functionality if slots become misaligned.
Solution: Use precision CNC machines and a robust design validation process.
- Material Weakening
Too much cutout can weaken the board.
Solution: Use reinforced materials or avoid too many cutouts.
- Manufacturing Costs
Advanced technology, such as laser cutting, incurs costs.
Solution: Cost-benefit ratios to be calculated according to volume and application in production.
Advantages of Using Advanced Technology for Slots and Cutouts
Advantages Manufacturers have with using advanced technology:
More accurate slotting and cutting ensure more performance
Unique shape and orientation of designs
Reduced Failure Rates
More resistance to breakage and wear at assembly and working.
At Blind Buried Circuits, our expertise in flexible PCB fabrication ensures that your designs incorporate high-quality slots and cutouts tailored to your requirements.
Comparison of Fabrication Techniques for Slots and Cutouts
| Technique | Precision | Cost | Best for |
| Drilling | High | Moderate | Small openings, prototypes |
| Routing | Medium | Moderate | Custom shapes, larger boards |
| Laser Cutting | Very High | High | Flexible PCBs, intricate designs |
| Punching | Low | Low (High setup) | High-volume production |