When working on a printed circuit board (PCB), you want your design to work every time. But things like sudden voltage changes can cause problems. This is where decoupling capacitors come in. They help your circuit stay stable. In this blog, you will learn why decoupling capacitors matter, how to use them, and what mistakes to avoid.
What Is a Decoupling Capacitor?
A decoupling capacitor is a small part that helps your circuit deal with voltage changes. It is placed between the power supply and the parts of the board that need steady voltage. If your circuit suddenly pulls too much power, the decoupling capacitor provides the extra energy quickly, helping your parts work properly.
You may also hear the term bypass capacitor. People sometimes confuse bypass with decoupling capacitors. They do similar things, but a bypass capacitor mainly blocks high-frequency signals from reaching sensitive parts, while a decoupling capacitor focuses more on keeping voltage steady. Still, many use the terms interchangeably.
Why Do You Need Them?
In a perfect world, the power that reaches your components will always be steady. But in real life, especially in fast-switching circuits, things change quickly. If a microcontroller or other part suddenly demands more power, the voltage can dip. This causes the part to behave strangely or even fail. Decoupling capacitors fixes this. They provide quick energy when the power line cannot react fast enough. Without them, you may face random errors in your PCB design, especially in digital circuits.
If you are working with a PCB board manufacturer or a PCB manufacturing assembly team, they’ll often recommend proper capacitor placement from the start. It’s that important.
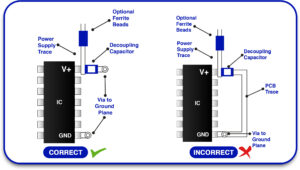
How Do They Work?
Think of a decoupling capacitor as a small battery near your component. It stores energy and releases it quickly when needed, keeping the voltage stable. Your circuit’s power line has resistance and inductance. That means energy doesn’t move instantly. So when one part of the board pulls a lot of current, the power supply might not be able to keep up in time. A decoupling capacitor helps by filling the gap.
These capacitors also filter out noise. High-frequency noise can make your circuit less reliable. Capacitors absorb this noise and keep it from reaching sensitive parts.
Choosing the Right Capacitor
The value of the decoupling capacitor you choose matters. Most people use 0.1 microfarad (uF) ceramic capacitors for digital chips. But depending on your circuit, you might also need values like 1 uF or 10 uF.Placement is also important. You want the capacitor close to the chip’s power and ground pins. The shorter the path, the better it works.
If you use a decoupling capacitor calculator, it can help you decide the right value for your design. But don’t rely on tools alone. Experience also matters. Testing with different values is a good way to learn what works.
How Many Should You Use?
You may need one capacitor for each power pin of a chip, depending on how much current the chip uses and how fast it switches. For high-speed chips, you might even need more than one capacitor, each with a different value.
Remember your entire PCB layout. If you’re working with a custom PCB manufacturer, they will often help you choose capacitor values and placement. A well-done PCB manufacturing and assembly plan includes all these details.
Where to Place Them?
Decoupling capacitor placement is key. Put them as close as possible to your IC’s power and ground pins. This reduces the path resistance and inductance.
If you place the capacitor too far, it won’t be as effective. In some designs, you may need to place multiple capacitors in different spots on the board.
In high-speed PCB board assembly manufacturing, even small changes in placement can affect performance. So be careful and double-check during your PCB layout.
Using Decoupling Capacitors in Complex Boards
Modern boards often have several chips. Some boards are part of robotics systems or advanced electronics. For example, a robotics PCB design may need many decoupling capacitors. That’s because robotic systems use a lot of power and switch signals quickly.
When you plan a PCB assembly robot or any high-end project, consider the number of capacitors you need. Talk to your PCB manufacturing company about best practices. They may guide you based on past projects.
Coupled Capacitors and Supply Capacitors
Sometimes, you’ll also hear about supply capacitors or coupled capacitors. These are used in similar ways, helping to manage voltage and reduce noise.
A supply capacitor usually has a higher value and is placed near the primary power input. A coupled capacitor helps connect different parts of a circuit while blocking unwanted signals.
Each has its job, but they all work to keep your circuit stable, so make sure you understand how they fit into your design.
Tips for Using Decoupling Capacitors
Here are some simple tips:
- Always place capacitors close to your chips
- Use a mix of values like 0.1 uF, 1 uF, and 10 uF for better coverage
- Keep your traces short between the capacitor and pin
- If possible, use surface-mount capacitors
- Talk to your PCB manufacturer about your plan
These small steps make a big difference in how well your circuit works.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Placing capacitors too far from the chip
- Using only one capacitor for a complex chip
- Ignoring layout in fast-switching circuits
- Not testing with different capacitor values
These mistakes can cause random failures that are hard to track. Good planning helps you avoid problems before they start.
What Happens Without Them?
Without decoupling capacitors, your board may fail. You might see voltage spikes or dips. Your microcontroller may reset or stop working. High-frequency signals can travel where they shouldn’t, causing noise in your system.
If you’re working with a PCB manufacturing company or planning to order a PCB board assembly manufacturing service, always ask if your layout has enough decoupling.
Final Thoughts
Decoupling capacitors are not just extra parts. They are critical to how well your board runs. You want stable voltage, clean signals, and low noise. These capacitors help you get that. When planning your next design, whether it’s a simple board or a complex project, make sure decoupling is included. If you’re unsure, ask your PCB manufacturer for advice. Their experience can save you from common mistakes.
Understanding how to use decoupling capacitors properly will help you build better, more reliable PCBs every time. Whether you use a decoupling capacitor calculator or rely on experience, this one step can make your designs stronger and more dependable