When you’re working with printed circuit boards (PCBs), every layer matters. One material that plays a significant role, but often gets overlooked, is prepreg. If you want your PCBs to last, run smoothly, and meet strict performance needs, then prepreg is something you can’t ignore. In this blog, you’ll learn why prepreg matters, how it fits into your board, and what to know when choosing it.
What is Prepreg in PCB Design?
Prepreg stands for “pre-impregnated” fiberglass cloth. It’s filled with resin that’s partially cured. Think of it like glue that’s dry to the touch but melts and hardens when heated. In PCB design, prepreg layers are sandwiched between copper-clad laminates. When you heat them during the PCB fabrication in the USA process, they melt, flow, and then harden to bond everything together.
This bonding is what keeps the board strong and stable. It’s essential when you stack multiple layers in your PCB. Without prepreg, the layers wouldn’t stick together right, and your board would be weak or even fail.

Why Does Prepreg Matter in PCB Quality?
If your prepreg material is of poor quality, the whole board suffers. Good prepreg ensures:
- Strong bonding between layers
- Stable thickness of the board
- Reliable insulation between copper traces
- Good electrical performance
In custom PCB production, where you build boards to fit exact needs, prepreg can affect how signals travel. If the spacing between copper layers isn’t proper, or if the prepreg doesn’t bond properly, you can have signal loss, heat buildup, or even total board failure.
Prepreg Material and Electrical Signals
Signals on your PCB travel fast, very fast. To keep them clear, the materials between copper layers must be consistent. Prepreg offers the insulation and spacing needed for this. It helps avoid:
- Signal delays
- Crosstalk between traces
- Loss of signal quality
So, if you’re building a board that deals with high-speed data, like in computers or telecom gear, your choice of prepreg really matters.
PCB Core vs Prepreg: What’s the Difference?
Let’s clear up a common confusion: PCB core vs prepreg.
- Core: A core is a fully cured laminate. It has copper on both sides and doesn’t change shape during heating.
- Prepreg: This is uncured and softens when heated. It’s used to bond two layers or cores together.
Both are essential. The core provides structure. The prepreg acts like glue. Together, they form the full board.
In core and prepreg in PCB design, the right balance helps achieve good mechanical strength and steady performance.
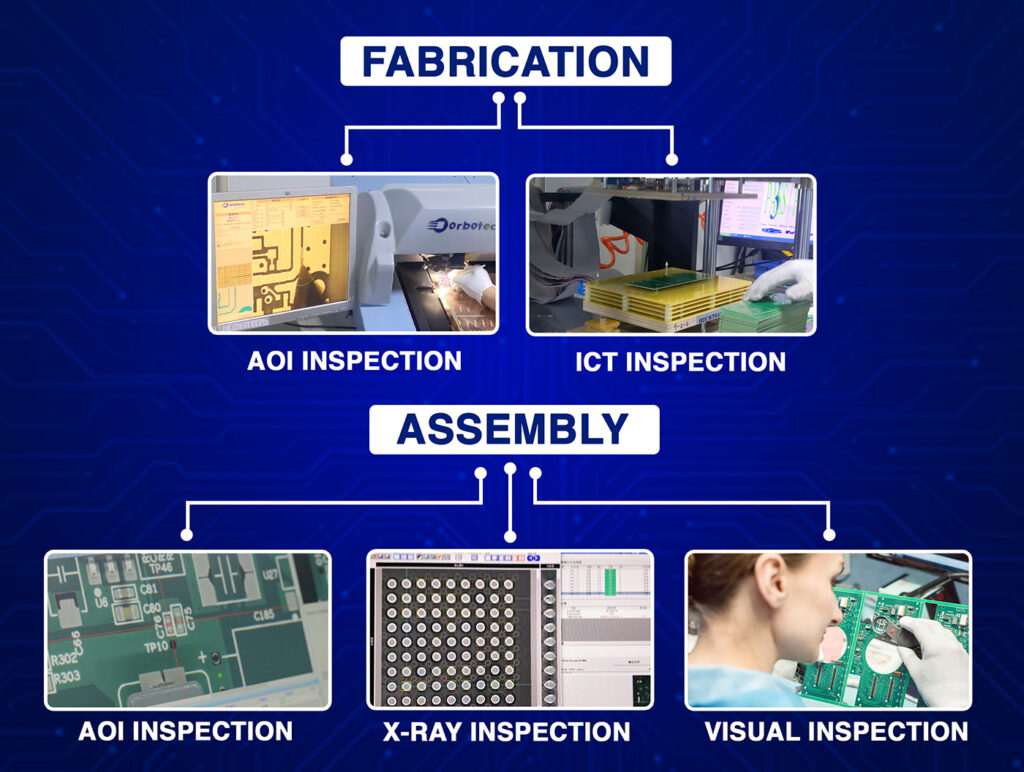
How Prepreg Is Used in PCB Fabrication USA
In the USA, PCB fabrication process, prepreg is placed between copper layers or cores. Then, the whole stack is heated and pressed. During this stage:
- The prepreg melts and flows
- It fills the gaps between copper features
- It hardens to form a solid, bonded board
If the prepreg doesn’t melt properly or has air bubbles, the board may have weak spots. These can cause the board to break under stress or fail during use. That’s why good PCB makers focus heavily on prepreg handling.
Things to Look for in Prepreg Materials
Not all prepreg is the same. When choosing a PCB manufacturer, you want one that uses high-quality prepreg. Here’s what to check:
- Glass transition temperature (Tg): A Higher Tg means the board can handle more heat.
- Resin content: The right amount ensures strong bonding.
- Flow characteristics: It should flow enough to bond layers but not overflow.
- Dielectric constant: This affects signal speed and quality.
When your board goes into a hot or high-power setup, these factors make a big difference.
Prepreg in Custom PCB Production
In custom PCB production, you can’t afford to guess. Every layer must do its job. Choosing the right prepreg can help you:
- Control board thickness
- Keep copper layers spaced just right
- Improve performance in signal-heavy boards
This is why good designers work closely with PCB manufacturers to pick the best prepreg for the job.
Common Prepreg Problems and How to Avoid Them
Some common issues include:
- Delamination: Layers separate because the prepreg didn’t bond well.
- Resin starvation: Not enough resin to fill all gaps.
- Excessive flow: Too much resin can overflow and cause shorts.
To avoid these, always work with a trusted PCB fabrication partner. Make sure they store prepreg correctly (in cold, dry places), use it before the expiry date, and control heat and pressure in the press cycle.
Core and Prepreg in PCB Stack-Up
In a multilayer PCB, you’ll have a mix of cores and prepreg. A typical setup might look like:
- Copper
- Prepreg
- Core
- Prepreg
- Copper
This structure lets you build boards with 4, 6, 8, or more layers. The more layers you need, the more important prepreg becomes.
Each layer must be flat, bonded, and spaced correctly. That’s what prepreg helps with.
Final Thoughts: Don’t Overlook Prepreg
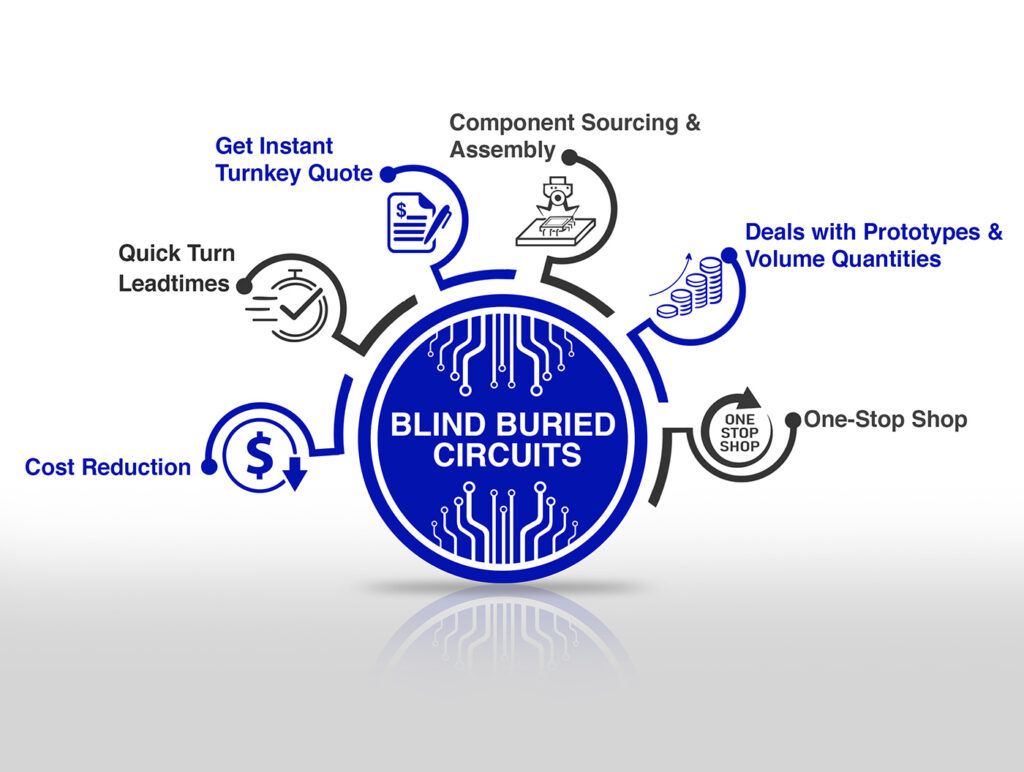
If you want strong, high-quality boards, prepreg isn’t something to ignore. It’s not just a filler, it’s what holds your board together and makes sure it works the way it should. When you’re talking to a PCB manufacturer or setting up your custom PCB production, ask questions about their prepreg process. The right prepreg choices can mean the difference between a reliable board and one that fails. This is especially true in advanced boards like Blind Buried Circuits, where spacing and bonding are critical. In those boards, prepreg is essential for proper stacking and keeping layers tightly sealed.
So, next time you plan your board, remember: prepreg matters a lot.